Researchers in Germany identified bone disease in the fossilized jaw of a Tyrannosaurus rex using a CT-based, nondestructive imaging approach, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The imaging method could have significant applications in paleontology, researchers said, as an alternative to fossil assessment methods that involve the destruction of samples.
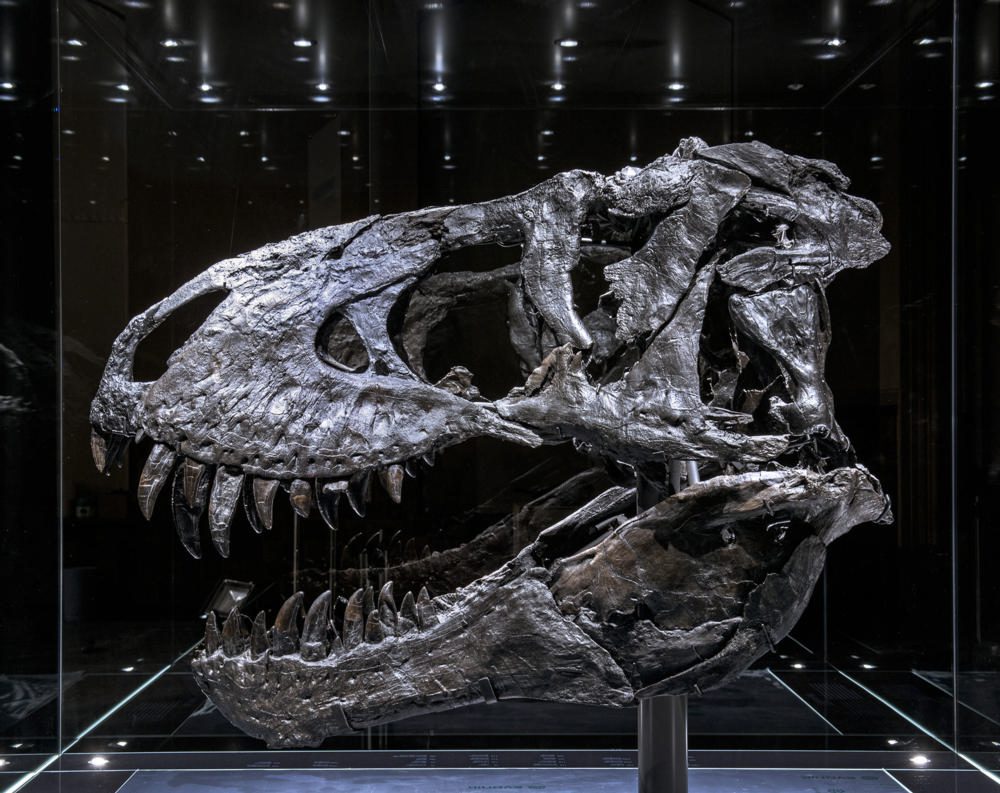
A familiar subject of today’s popular culture, the T. rex was a massive, carnivorous dinosaur that roamed what is now the western United States millions of years ago. In 2010, a commercial paleontologist working in Carter County, Montana, discovered one of the most complete T. rex skeletons ever found. The fossilized skeleton dates back approximately 68 million years to the Late Cretaceous period. It was sold to an investment banker, who dubbed it “Tristan Otto” before loaning it out to the Museum für Naturkunde Berlin in Germany. It is one of only two original T. rex skeletons in Europe.

Charlie Hamm, M.D., a radiologist at Charité University Hospital in Berlin, and his colleagues recently had an opportunity to investigate a portion of the Tristan Otto’s lower left jaw. While previous fossil studies have mostly relied on invasive sampling and analysis, Dr. Hamm and colleagues used a noninvasive approach with a clinical CT scanner and a technique called dual-energy computed tomography (DECT). DECT deploys X-rays at two different energy levels to provide information about tissue composition and disease processes not possible with single-energy CT.
“We hypothesized that DECT could potentially allow for quantitative noninvasive element-based material decomposition and thereby help paleontologists in characterizing unique fossils,” Dr. Hamm said.
The CT technique enabled the researchers to overcome the difficulties of scanning a large portion of Tristan Otto’s lower jaw called the left dentary. The piece’s high density was particularly challenging, as CT imaging quality is known to suffer from artifacts, or misrepresentations of tissue structures, when looking at very dense objects.
“We needed to adjust the CT scanner’s tube current and voltage in order to minimize artifacts and improve image quality,” Dr. Hamm said.
On visual inspection and CT imaging, the left dentary showed thickening and a mass on its surface that extended to the root of one of the teeth. DECT detected a significant accumulation of the element fluorine in the mass, a finding associated with areas of decreased bone density. The mass and fluorine accumulation supported the diagnosis of tumefactive osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone.
“While this is a proof-of-concept study, noninvasive DECT imaging that provides structural and molecular information on unique fossil objects has the potential to address an unmet need in paleontology, avoiding defragmentation or destruction,” Dr. Hamm said.
“The DECT approach has promise in other paleontological applications, such as age determination and differentiation of actual bone from replicas,” added Oliver Hampe, Ph.D., senior scientist and vertebrate paleontologist from the Museum für Naturkunde Berlin. “The experimental design, including the use of a clinical CT scanner, will allow for broad applications.”
Dr. Hamm and his colleagues also collaborated with paleontologists from the Chicago’s Field Museum and colleagues from the Richard and Loan Hill Department of Biomedical Engineering at the University of Illinois at Chicago to perform a CT analysis of the world-famous T. rex “Sue” that is housed in the museum.
“With every project, our collaborative network grew and evolved into a truly multidisciplinary group of experts in geology, mineralogy, paleontology and radiology, emphasizing the potential and relevance of the results to different scientific fields,” Dr. Hamm said.
Additional co-authors are Patrick Asbach, M.D., Torsten Diekhoff, M.D., and Lynn Savic, M.D.