January 22, 2021
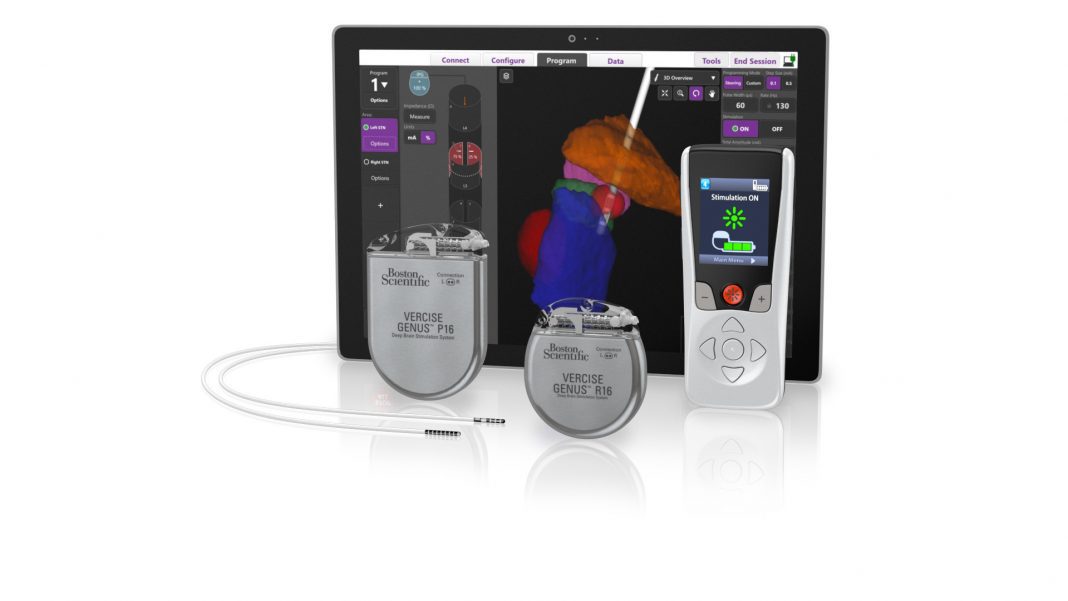
Vercise Genus Deep Brain Stimulation System (fourth generation) has received FDA approval reports Boston Scientific.
More than 10 million people worldwide are living with Parkinson’s disease (PD) – a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder, which causes stiffness, slowness and tremors due to a decrease of dopamine in the brain.ii DBS devices – and specifically the Vercise Genus Deep Brain Stimulation System, can treat the symptoms of PD by delivering targeted electrical stimulation via surgically-implanted leads in the brain connected to an IPG. Devices can either be rechargeable or non-rechargeable based on patient and physician preference, and while many patients appreciate the long battery life available with a rechargeable system, approximately 80 percent of DBS devices used globally today are non-rechargeable.iii
“We have used the Vercise Gevia System with the Cartesia Directional Leads to provide our patients with a small device, a battery life of at least 15 years and optimal symptom control by delivering the right dose of stimulation precisely where it’s needed,” said Jill Ostrem, medical director and division chief, University of California, San Francisco Movement Disorders and Neuromodulation Center. “Now, the latest generation Genus portfolio – with an MR-compatible non-rechargeable IPG as well – provides greater access to patients who might not be candidates for a rechargeable system.”
The fourth generation of the DBS system since 2012, Vercise Genus Deep Brain Stimulation System builds upon rapid and meaningful innovations in battery longevity, directionality, and stimulation capabilities. Through a strategic collaboration, the Brainlab platform provides enhanced visualization capabilities that enable clinicians to see lead placement within the context of each patient’s segmented target anatomy.
“We continue to prioritize therapy innovations that improve our patients’ quality of life with a wide range of personalized offerings,” said Maulik Nanavaty, senior vice president and president, Neuromodulation, Boston Scientific. “For people living with movement disorders, this means developing new technologies that are designed to refine motor control, reduce programming times and expand MR compatibility to improve their treatment experience and ultimately their daily living.”
The company commenced the European launch of the Vercise Genus System in September 2020 and expects to begin a controlled U.S. launch in the coming months. The Vercise Genus Deep Brain Stimulation System is indicated for use in the bilateral stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN) as an adjunctive therapy in reducing some of the symptoms of moderate to advanced levodopa-responsive PD that are not adequately controlled with medication. The system is also indicated for use in the bilateral stimulation of the internal globus pallidus (GPi) as an adjunctive therapy in reducing some of the symptoms of advanced levodopa–responsive PD that are not adequately controlled with medication.