AI Can Detect Lung Nodules: A new study has been unveiled at the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC) 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancerin San Diego, CA citing promising initial results using AI-powered chest X-ray interpretation to detect pulmonary nodules which could develop into early-stage lung cancers long before symptoms appear. The retrospective study demonstrated via interim results, an average diagnostic delay of nearly three years from the first abnormal chest X-ray.
The study conducted at the Phrapokklao Hospital’s Cancer Centre of Excellence in Bangkok, Thailand was led by Dr Passakorn Wanchaijiraboon, Medical Oncologist and Deputy Director using the Qure.ai chest X-ray AI solution qXR.
Dr. Passakorn Wanchaijiraboon, while unveiling the poster, said;
“This abstract study, presented at the World Conference on Lung Cancer, provides a snapshot of the significant potential that AI-assisted chest X-ray analysis holds for transforming early cancer detection and reducing the rate of missed lung cancer diagnoses. In most Thai government hospitals, chest X-rays are interpreted by non-radiologists. However, in community hospitals, there are often no radiologists available to read chest X-rays at all. By overlaying specialist AI to read all cases, we can support clinicians in detecting incidental high-risk nodules that may lead to lung cancer. This approach can streamline decision-making and potentially improve patient survival through the earlier diagnosis of cancer. The implementation of CXR AI is particularly beneficial in the context of community hospitals, where it can significantly enhance diagnostic capabilities in the absence of on-site radiologists.”
The Phrapokklao Cancer Centre study retrospectively reviewed and evaluated the chest X-ray image database of newly diagnosed lung cancer patients over an annual period using qXR. Missed lung cancer was defined as missed in the original report six months prior to a definitive lung cancer diagnosis. 18% of patient cases were found to have a missed lung cancer diagnosis over an average period of nearly three years (32.3 months), with a maximum duration of over eight years (96 months) and minimum eight months. Half the patient cases had chest X-rays taken for non-respiratory symptoms as part of a health check-up, categorising them as ‘incidentally detected’.
Bhargava Reddy, Chief Business Officer, Oncology at Qure.ai
“This is an exciting evidence example that underscores the transformative potential of AI in the fight against lung cancer. Overlaying AI on chest X-rays casts the net wider by proactively triaging patients for the risk of lung cancer. It goes beyond people with symptoms or qualifying for screening initiatives based on age or smoking history, to currently invisible and unprofiled patient populations thus detecting lung cancers earlier.”
Lung Cancer has one of the poorest survival outcomes of all cancers, with over two-thirds of patients diagnosed at an advanced stage, when curative treatment is no longer feasible1. Missed lung cancer is a source of concern for clinicians and an important medicolegal challenge2. Missed nodules resulting from lung cancer are the third most common reason for malpractice claims 3.
IASLC 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer hosted by the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (#WCLC24) is being held September 7 to 10 in San Diego, California. The Phrapokklao Cancer Centre study poster abstract presented can be viewed here: https://www.qure.ai/evidence/The-potential-of-chest-X-ray-Al-in-detecting-missed-lung-cancer-diagnosis-in-a-community-based-cancer-center-in-thailand
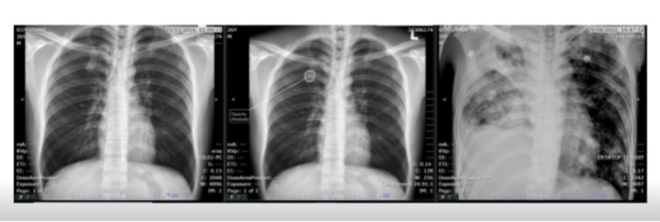
1st image Prior Chest X ray 2nd Image AI result 3rd Image Chest X ray at diagnosis
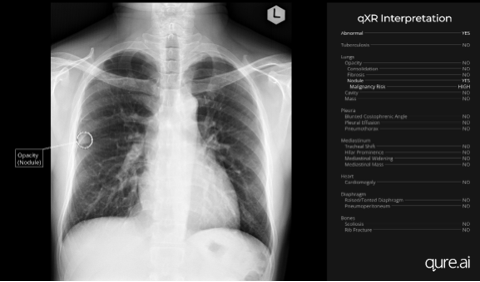
References
1,2 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5338577/
3 – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9431813/