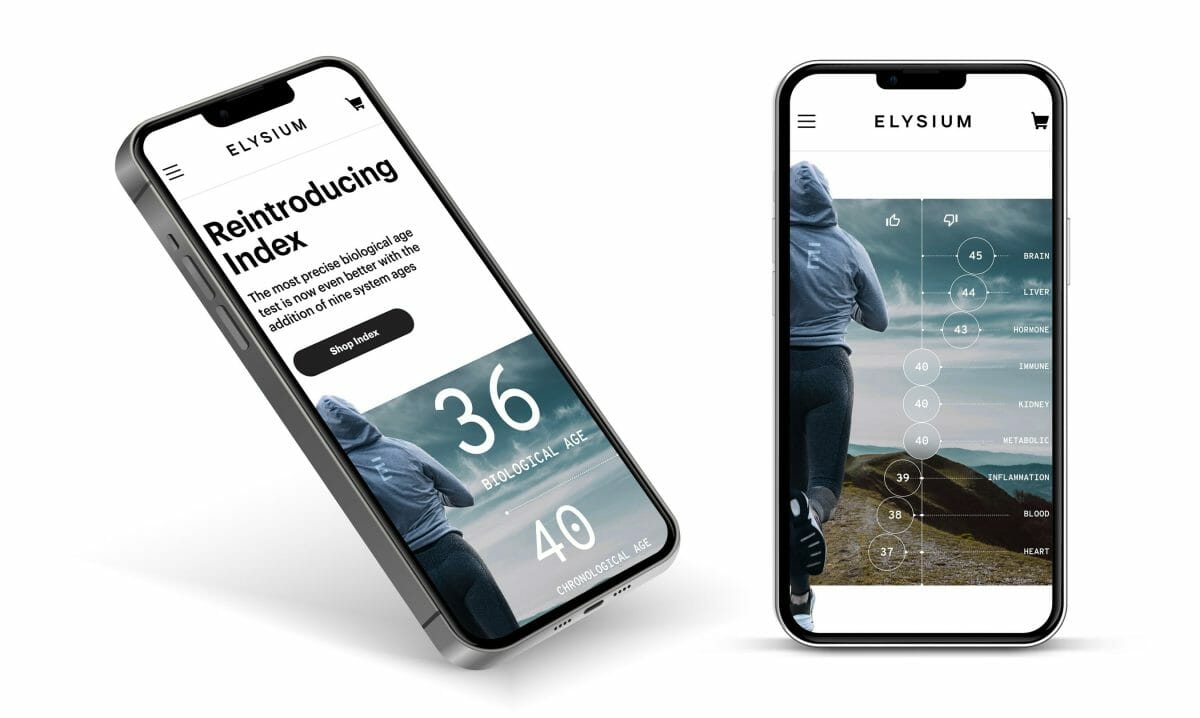
Elysium Health, Inc., a leading life sciences company focused on aging, today announced the addition of nine new measures of aging to its leading biological age test INDEX™ alongside the launch of the Aging Research Center by Elysium Health, both of which are firsts in the longevity field.
Already the most precise biological age test available compared to other published epigenetic measures of aging, and utilizing superior technology demonstrated in Nature Aging, Index now measures the ages of nine systems–brain, liver, metabolic, immune, heart, hormone, kidney, inflammation, and blood. Elysium Health is pleased to be the first company to offer this level of novel in-depth insight.
The study of epigenetics is at the forefront of research in the field of aging, and biological age is becoming a leading standard to measure overall health and wellness. Despite these advancements, progress has been restricted by human datasets that are disconnected, mostly inaccessible, and that fail to comprehensively represent diverse populations. With the launch of the Aging Research Center–a digitally-native research effort–Elysium Health aims to better our collective understanding of aging by building the world’s most actionable epigenetic dataset, with an emphasis on translation, comprehensiveness, and diversity. Through collaboration with the Elysium community, the Aging Research Center will provide consumers with the first-ever opportunity to participate directly in longevity research, enabling greater public access to breakthroughs in the field.
“Epigenetic clocks have been a major advance for the aging field, as they enable the precise study of biological aging without requiring a protracted timeline,” said Elysium Health chief scientist and MIT professor Leonard Guarente, Ph.D. “For consumers, Index was the first and most precise aging measure, and remains the only product to render a simple, saliva-based biological age test. The addition of nine systems extends this concept to measure aging in specific pathways, which provide even more useful information for making lifestyle changes to improve health. Leveraging this novel technology through the Aging Research Center offers the exciting opportunity to greatly accelerate breakthroughs in the field of aging by collaborating directly with consumers who opt in and have the greatest potential benefit to gain.”
The Aging Research Center will debut with a landmark prospective aging study–the Translational Initiative to Map Epigenetics in Aging (TIME-A). TIME-A aims to further our understanding of the connections between epigenetics, lifestyle, demographics, and health and aging, and was designed with the direction and advice of an expert researcher in prospective cohort studies Meir Stampfer, M.D., Dr.P.H., research professor of epidemiology and nutrition at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, co-principal investigator of the Nurses’ Health Study, Elysium Health Scientific Advisory Board member, and founding co-investigator of the Nurses’ Health Study II, the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study, and the Physician’s Health Studies I and II. Findings from TIME-A will support Elysium Health and its collaborators in their work to develop new epigenetic measures of health and disease, create tools for monitoring longevity and health, advance the development of truly personalized health programs and disease prevention protocols, and identify lifestyle factors that impact aging, while providing transformative, first-of-their-kind insights to study participants.
“Working with the Nurses’ Health Studies has not only been rewarding as a researcher and physician, but also incredibly significant from a public health perspective, advancing our understanding of cardiovascular disease, cancer, reproductive health, and more–something that the founding researchers could not have predicted at the outset,” said Dr. Stampfer. “These studies have collected information on lifestyle and health outcomes of 237,000 women since 1976, with millions of data points, and well over 1,500 papers in the scientific literature. I am optimistic that TIME-A can achieve important advances for the field of aging, especially given its digital architecture and the population of individuals who want to be a part of research in the field of longevity.”
As with TIME-A, future studies will engage Elysium’s renowned Scientific Advisory Board and extensive scientific network, and may include circadian disruption and sleep, female and male fertility, neuroplasticity, diet and cardiovascular health, physical performance, happiness and loneliness, and environmental exposure and stress. Studies are developed in collaboration with leading researchers and clinicians and integrate the latest tools in epigenetics, AI and machine learning, wearables, validated questionnaires, and other assessments. TIME-A is an observational, prospective study in which all Index users are eligible to enroll, and it will remain ongoing. Study participants are encouraged to take an Index test at least once every two years and to complete online surveys as they are scheduled.