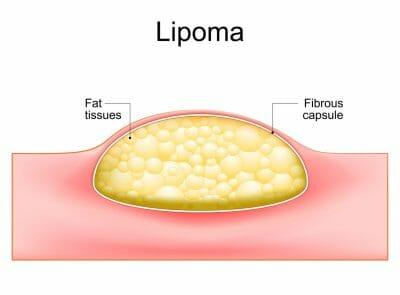
Lipomas are benign tumors that develop from fatty tissue. Although they are usually harmless, lipomas can cause discomfort or be unsightly, leading some patients to seek surgical removal. In this article, we will discuss the procedure for lipoma removal, as well as recovery and aftercare tips for patients.
Surgical removal is the most common method for removing lipomas. During the procedure, a surgeon will make a small incision and remove the lipoma from beneath the skin. In some cases, the surgeon may use liposuction to remove the fatty tissue. Lipoma removal surgery is typically an outpatient procedure, and patients can usually go home the same day.
After the surgery, patients will need to take care of the incision site to prevent infection and promote healing. This may include keeping the area clean and dry, avoiding strenuous activity, and taking any prescribed medications. With proper care, most patients can expect to fully recover within a few weeks.
Understanding Lipoma
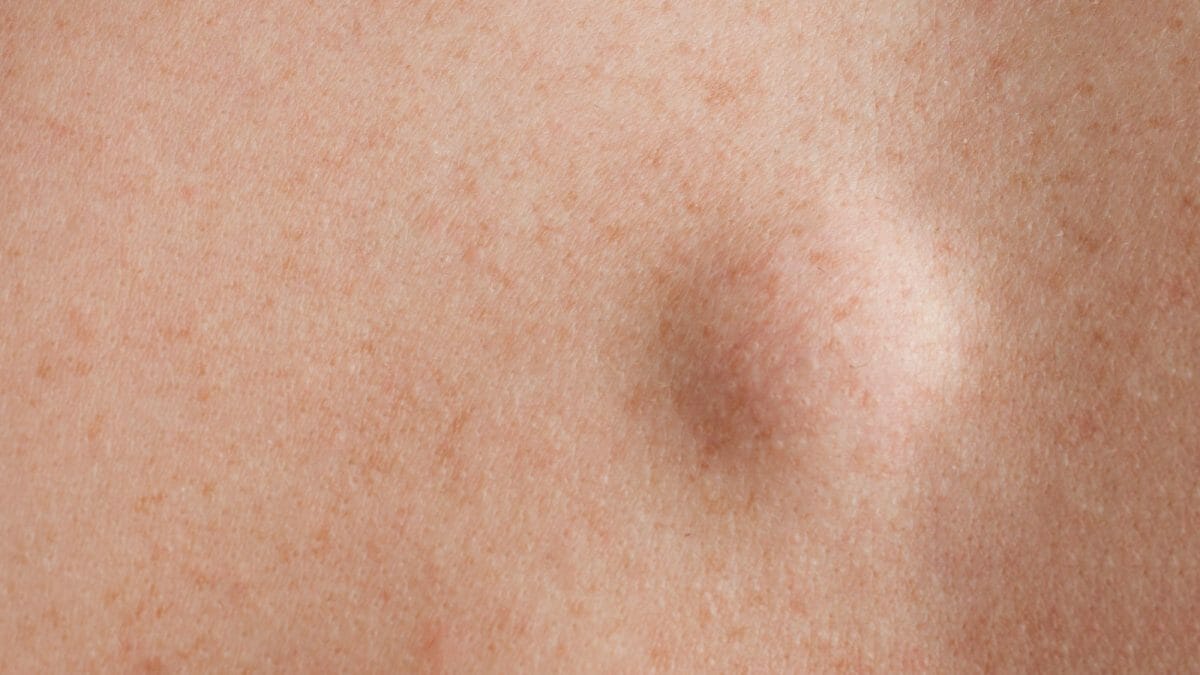
Lipomas are benign tumors made up of fatty tissue. They are usually small, soft, and painless, and can occur anywhere on the body where there is fat tissue. While they are not usually dangerous, they can sometimes grow large enough to cause discomfort or affect mobility.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Lipomas are usually discovered during a physical examination, as they can be felt under the skin. They are typically small, ranging from the size of a pea to a few centimeters in diameter. Lipomas are usually soft and moveable, and may be painful if they are located near a nerve.
If a lipoma is suspected, a doctor may order imaging tests, such as an ultrasound or MRI, to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, a biopsy may be needed to rule out other conditions.
Location and Size
Lipomas can occur anywhere on the body, but are most commonly found on the neck, shoulders, back, and arms. They can also occur on the thighs, abdomen, and chest. The size of a lipoma can vary, from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter.
Lipomas that are located near a joint or nerve can sometimes cause discomfort or affect mobility. In rare cases, lipomas can grow large enough to cause cosmetic concerns or interfere with normal bodily functions.
Overall, lipomas are a common and generally harmless condition. However, if you are experiencing symptoms such as pain or discomfort, or if you are concerned about the appearance of a lipoma, it is important to consult with a doctor to determine the best course of treatment.
Lipoma Removal Procedures
When it comes to removing lipomas, there are several procedures available that provide complete elimination of a lipoma. The most common procedures are surgical excision, liposuction, and minimally invasive techniques. Each procedure has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of procedure will depend on the size, location, and number of lipomas, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Excision
Surgical excision is the most common procedure for removing lipomas. It involves cutting into the skin and removing the lipoma along with its capsule. This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, but sedation may also be used for larger lipomas or for patients who are anxious.
After the procedure, the incision is closed with sutures or surgical glue, and a sterile dressing is applied. The patient can usually go home the same day, but recovery time can vary depending on the size and location of the lipoma.
Liposuction
Liposuction is another option for removing lipomas. This procedure involves making a small incision and using a thin, hollow tube called a cannula to suction out the fatty tissue. Liposuction is typically used for smaller lipomas that are located close to the skin surface.
Liposuction is usually performed under local anesthesia, and the patient can usually go home the same day. Recovery time is generally shorter than with surgical excision, but there may be some bruising and swelling in the treated area.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
In addition to surgical excision and liposuction, there are several minimally invasive techniques that can be used to remove lipomas. These techniques include laser removal, cryotherapy, and injection lipolysis.
Laser removal involves using a laser to break up the lipoma into small pieces, which are then removed through a small incision. Cryotherapy involves freezing the lipoma with liquid nitrogen, causing it to shrink and die off. Injection lipolysis involves injecting a solution into the lipoma to dissolve the fatty tissue.
Minimally invasive procedures are generally less invasive than surgical excision or liposuction, and they may be a good option for patients who have multiple small lipomas or who are not good candidates for surgery. However, these procedures may not be as effective as surgical excision or liposuction for larger or deeper lipomas.
Overall, the choice of procedure will depend on a variety of factors, including the size, location, and number of lipomas, as well as the patient’s overall health and preferences. We will work with each patient to determine the best course of treatment for their individual needs.
Preparation for Lipoma Removal
Before undergoing lipoma removal surgery, it is important to take certain steps to ensure a safe and successful procedure. In this section, we will discuss the necessary preparations patients should make before their surgery.
Medical Consultation
The first step in preparing for lipoma removal is to schedule a consultation with a medical professional. During this appointment, we will discuss the procedure in detail, including any potential risks and complications. We will also review your medical history and current medications to determine if you are a good candidate for surgery.
Pre-Surgery Medications
In some cases, we may recommend that patients stop taking certain medications in the days leading up to their surgery. This may include blood thinners or other medications that can increase the risk of bleeding during the procedure. Patients should always follow their doctor’s instructions regarding medication use before surgery.
Hygiene Preparations
To reduce the risk of infection, patients should take certain hygiene precautions before their surgery. This may include showering with antibacterial soap the night before the procedure and avoiding lotions, perfumes, and other scented products that can increase the risk of infection. Patients should also wear clean, loose-fitting clothing to their appointment.
By following these preparation guidelines, patients can help ensure a successful lipoma removal surgery. If you have any questions or concerns about preparing for your procedure, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Post-Removal Recovery
After a lipoma removal surgery, it is essential to follow proper aftercare instructions to ensure a smooth and speedy recovery. In this section, we will discuss some of the most important aspects of post-removal recovery, including managing pain, wound care, and medication use.
Managing Pain
It is common to experience some pain and discomfort after a lipoma removal surgery. We recommend using ice packs to help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 20 minutes at a time, several times a day, for the first 48 hours after surgery.
Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen can also help manage pain. However, it is important to speak with your doctor before taking any medication to ensure that it is safe and appropriate for you.
Wound Care
Proper wound care is crucial for preventing infection and promoting healing. We recommend keeping the surgical site clean and dry for the first 24 to 48 hours after surgery. After that, you can gently clean the area with soap and water and pat it dry.
Your doctor may also recommend using a sterile dressing or bandage to cover the surgical site. Be sure to change the dressing regularly and follow your doctor’s instructions for when and how to remove it.
Medication Use
Your doctor may prescribe medication to help manage pain or prevent infection after surgery. It is important to take any prescribed medication exactly as directed and to finish the entire course of treatment, even if you start feeling better.
If you experience any side effects from your medication or have any concerns, be sure to contact your doctor right away.
In summary, proper aftercare is essential for a smooth and speedy recovery after a lipoma removal surgery. By managing pain, practicing good wound care, and following medication instructions, you can help ensure a successful recovery.
Possible Complications and Risks
Lipoma removal is generally a safe procedure, but like any surgery, there are potential risks and complications. It is important to discuss these with your doctor before the procedure so that you are fully informed.
Scarring
Scarring is a common complication of lipoma removal. The size and location of the incision will determine the severity of the scar. In most cases, the scar will fade over time and become less noticeable. However, in some cases, the scar may be more prominent and require additional treatment to reduce its appearance.
Infection
Infection is a rare but possible complication of lipoma removal. It is important to keep the incision site clean and dry to prevent infection. Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, and discharge from the incision site. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Recurrence of Lipoma
There is a small chance that the lipoma may grow back after removal. This is more likely if the entire lipoma was not removed or if there were multiple lipomas in the same area. If you notice a lump in the same area after the procedure, contact your doctor.
Bleeding
Bleeding is a rare but possible complication of lipoma removal. Your doctor will use techniques to minimize bleeding during the procedure. However, if bleeding occurs after the procedure, it is important to contact your doctor immediately.
Overall, the risks and complications of lipoma removal are minimal. By following your doctor’s instructions for aftercare, you can minimize the risk of complications and ensure a smooth recovery.
Preventing Lipoma Recurrence
After undergoing lipoma removal surgery, patients may wonder how to prevent the growth and recurrence of lipomas. Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent lipoma recurrence, there are some steps that patients can take to reduce the likelihood of recurring lipomas.
Diet and Supplements
Maintaining a healthy diet and taking certain supplements may help prevent the recurrence of lipomas. A diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in processed foods and saturated fats, may help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. Additionally, taking supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and probiotics may also help reduce inflammation and boost the immune system.
Avoiding Trauma
Trauma to the skin and underlying tissue may increase the risk of developing lipomas. Therefore, it is important to avoid activities that may cause trauma to the affected area. Patients should also be cautious when engaging in activities that may cause trauma to other parts of the body, as trauma to one area may affect other areas of the body as well.
Fibrous Capsule
Lipomas are often encapsulated in a fibrous capsule, which may contribute to their growth and recurrence. To prevent the recurrence of lipomas, it is important to ensure that the entire fibrous capsule is removed during the initial surgery. In some cases, a small amount of the capsule may be left behind to avoid damaging surrounding tissue, but this increases the risk of recurrence.
In conclusion, while there is no guaranteed way to prevent the recurrence of lipomas, maintaining a healthy diet, taking certain supplements, avoiding trauma, and ensuring that the entire fibrous capsule is removed during surgery may help reduce the likelihood of recurring lipomas. If you have any concerns about lipoma recurrence, please consult with your doctor.