Lunit
Lunit (KRX:328130.KQ), a leading provider of AI-powered solutions for cancer diagnostics and therapeutics, today announced the publication of a new study, highlighting the effectiveness of Lunit INSIGHT MMG in significantly reducing radiologists’ workload while enhancing cancer detection rates.
Published in European Radiology
Conducted in collaboration with researchers from Acibadem Mehmet Ali Aydinlar University, Marmara University, Namik Kemal University, and Istanbul University, Türkiye, the study result was recently published in European Radiology, the flagship journal of the European Society of Radiology (ESR).
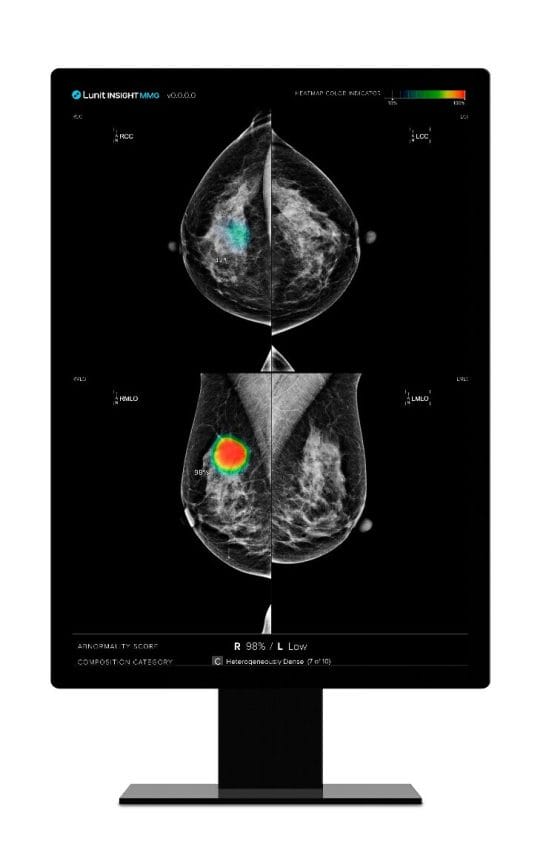
This comprehensive study encompassed over 22,621 mammograms from 8,825 women over a decade. Utilizing Lunit INSIGHT MMG, Lunit’s AI-powered solution for breast cancer detection, the research aimed to assess its proficiency in early cancer detection within a breast cancer screening program.
A pivotal finding of the study is Lunit INSIGHT MMG’s potential to reduce workload by nearly 70% through a hybrid workflow scenario that categorizes mammograms into immediate review, further evaluation, or no action needed based on AI-assessed risk scores, alongside a 30.5% boost in cancer detection accuracy. This indicates a substantial step forward in improving the efficiency of breast cancer screening programs, potentially enabling broader screening coverage and reducing the burden on healthcare systems.
The study further revealed that the AI system identified 51.72% of interval cancers, and 50% of missed cancers. Additionally, the study illustrated that using Lunit INSIGHT MMG as a second reader could potentially expedite the diagnosis by an average of nearly 30 months, compared to traditional screening methods.
Brandon Suh, CEO of Lunit
“This study not only reaffirms Lunit INSIGHT MMG’s efficacy in detecting breast cancer early but also illuminates its impact on operational efficiency and economic value within healthcare systems. For years, most of the conversation around AI in medical diagnostics has centered on its medical efficacy. However, this research showcases how AI can streamline workflows, reduce the radiological burden, and potentially offer significant cost and time savings. As we move forward, our focus will be on harnessing these dual benefits of AI – enhancing medical outcomes while also driving economic efficiency. We’ll expand our research and development efforts to further integrate AI in ways that not only maximize the quality of care but also the sustainability of healthcare systems.”