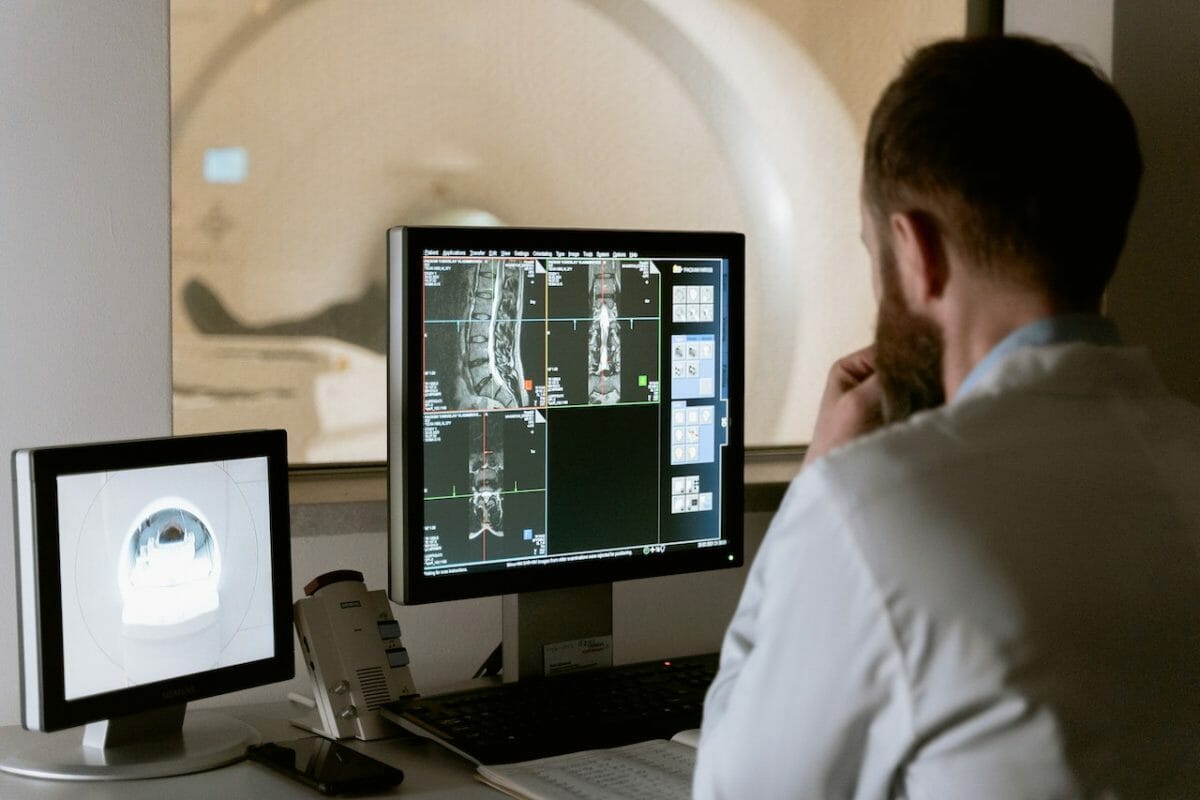
Medical imaging has evolved significantly since the introduction of X-rays in the late 1800s. Today, it’s an invaluable tool for healthcare professionals in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating various conditions. As technology has advanced, we’ve seen significant improvements in the quality and clarity of medical images. However, capturing flawless visuals can be challenging due to patient movement, inadequate contrast, or equipment limitations. This is where digital enhancement tools become invaluable.
Healthcare professionals constantly seek more accurate diagnoses, which requires high-quality visuals. Clear, sharp, and detailed medical visuals are indispensable assets for clinicians. But obtaining such visuals can be tricky, given the numerous physical and technological barriers. This is why enhancement tools have become crucial in today’s medical toolkit, enabling professionals to extract the maximum diagnostic information from their images.
In this article, we will explore the role of digital enhancement tools in the medical imaging field, how they improve the quality of visuals, and the implications of their use for diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
The Digital Revolution in Medical Imaging
In this digital age, editing tools are vital in diagnostics and research. These tools enable healthcare professionals to concentrate on important visual parts, enhance the visibility of structures, and even construct composite images for a clearer view. All of these facilitate accurate diagnoses.
It’s worth emphasizing that these editing tools should be used cautiously in the medical field. While they can help improve visuals for better diagnoses, using them responsibly is essential to retain the originals’ integrity and authenticity. Misusing or unethically using these tools can result in misdiagnoses and serious patient repercussions.
The growing demand for high-quality medical images has prompted many software providers to develop specialized editing tools tailored to the specific needs of the medical community. These tools come with features, such as AI-powered enhancements that can automatically improve quality, that are particularly helpful for busy professionals. Nonetheless, it is vital for healthcare professionals to choose reputable and reliable tools designed for medical applications and to use them responsibly to guarantee accurate and ethical diagnoses.
Exploring Quality Enhancement
Contrast increaser tools are essential for enhancing medical images, making detecting and diagnosing health conditions easier. These tools can be particularly valuable when the initial visuals are of subpar quality due to poor lighting, patient movement, or equipment limitations. By enhancing contrast, these tools help uncover details, enabling healthcare professionals to make more informed decisions.
AI-powered tools have brought remarkable advancements in improving contrast. For instance, the online image editor by Luminar Neo leverages AI technology to adjust and enhance contrast in photographs automatically. Although not explicitly designed for medical applications, the technology behind such tools showcases the progress that could be applied to medical imaging.
As always, using enhancement tools responsibly and ethically in a medical context is crucial, preserving the originals’ integrity and ensuring accurate and reliable diagnoses.
The Ethics of Enhancement in Medical Imaging
The integrity of diagnostic visuals is paramount. Any alterations must be carried out responsibly and ethically. When using tools to enhance quality, it’s essential to ensure that the modifications do not distort the vital information present in the original. Misrepresenting or changing the true state can result in misdiagnoses and potentially harmful treatment decisions.
Guidelines for Responsible Editing
Healthcare professionals should follow certain guidelines when editing medical images:
- Transparency: Document any modifications made to an image clearly in the patient’s medical record, including the tools used, the adjusted parameters, and the reasons for the edits.
- Relevance: Make only necessary and pertinent modifications. Editing should be used to improve clarity for diagnostic purposes, not to manipulate or misrepresent.
- Skill and Expertise: Trained professionals who comprehend the implications of the changes should perform editing. It is vital to balance enhancement and preservation of the original information.
- Compliance: Adhere to ethical guidelines and professional standards set by relevant medical organizations when editing.
Conclusion
The future of medical imaging holds great promise with integrating AI and machine learning. These innovations are set to revolutionize how we enhance diagnostic images, improving accuracy and patient outcomes. As healthcare professionals adopt these advanced technologies, it’s essential to strike a balance between leveraging their benefits and preserving trust and authenticity in the field.
We’re entering an exciting new era in diagnostics, but with great power comes great responsibility. The medical community must be mindful of using these advanced tools ethically and responsibly, ensuring that the original integrity of diagnostic images is maintained. By using these technologies wisely, we can enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient care without sacrificing the trust and authenticity that are so crucial in medical imaging.