In the ever-evolving landscape of modern medicine, one revolutionary field has played a pivotal role in diagnosis, treatment, and research: Medical Imaging Technology. Each year, advancements in this domain have brought remarkable breakthroughs, pushing the boundaries of what was once thought possible. From the historic discovery of X-rays to the cutting-edge realms of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT), and other innovative imaging modalities, medical professionals have been equipped with powerful tools that have transformed patient care and medical understanding. Engage with Managed Security Services providers to leverage medical imaging technology in your healthcare industry.
This comprehensive overview will delve into why medical imaging is important and remarkable advancements in these imaging modalities, showcasing their indispensable role in modern healthcare.
What is Medical Imaging Technology?
Medical Imaging Technology refers to a branch of healthcare science and technology that involves various advanced imaging techniques to visualize the internal structures and functions of the human body. These non-invasive imaging modalities are crucial in diagnosing, monitoring, and guiding treatment for various medical conditions. Medical imaging technologies allow healthcare professionals, including radiologists, physicians, and surgeons, to gain valuable insights into anatomical details, detect abnormalities, and assess the progression of diseases without the need for invasive procedures. If you want to consider medical imaging technology for your healthcare industry, contact our Cybersecurity Audit experts.
There are several critical medical imaging modalities, each offering unique benefits and applications. X-ray imaging is one of the oldest and most widely used techniques, which utilizes low-dose ionizing radiation to produce images of bones and soft tissues. Computed Tomography (CT) scans, on the other hand, provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body, enabling the visualization of organs, blood vessels, and various pathological conditions with enhanced clarity and precision.
X-ray Imaging: Pioneering the Path to Diagnosis
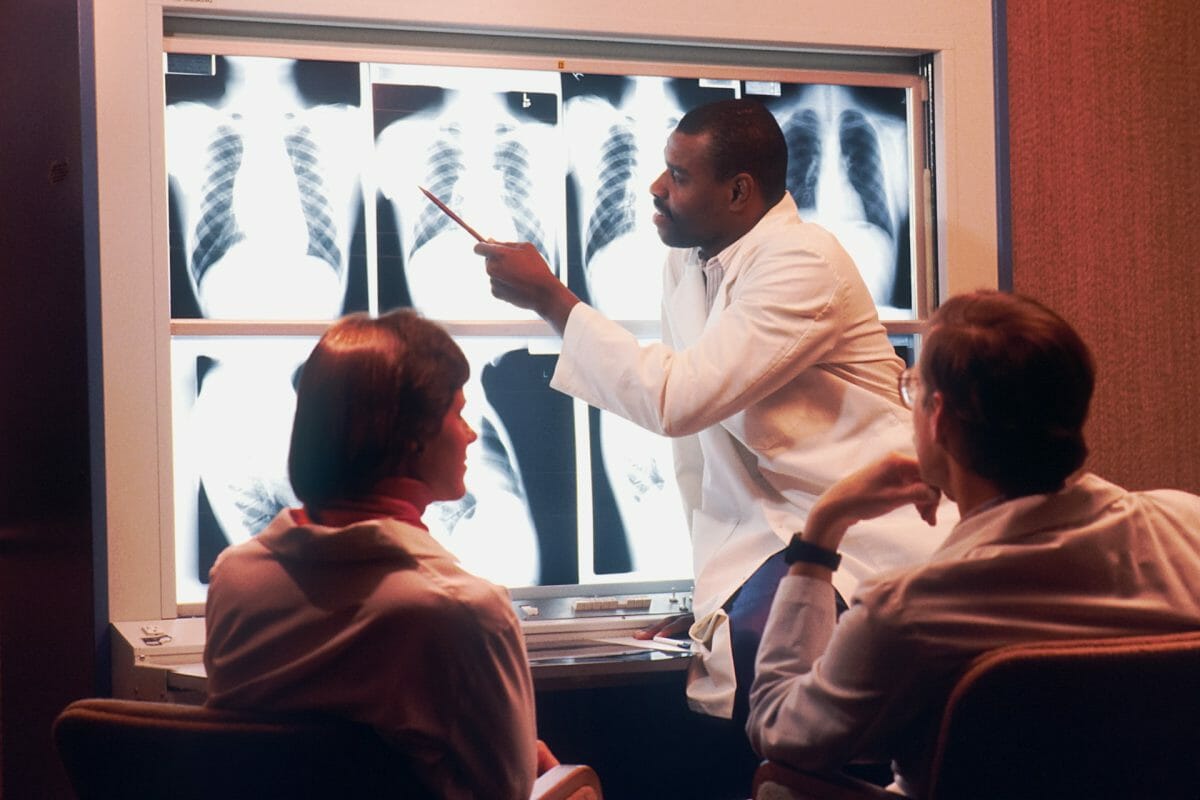
X-ray imaging has played a pivotal role in revolutionizing the field of medical diagnosis. X-rays have allowed healthcare professionals to detect and diagnose various conditions and injuries by utilizing electromagnetic radiation to capture images of the body’s internal structures. With its ability to penetrate soft tissues and capture detailed images of bones, X-ray technology has become essential in different medical disciplines, including orthopedics, dentistry, and cardiology.
The diagnostic capabilities of X-ray technology have been greatly enhanced over the years through advancements such as digital radiography and computed tomography (CT) scans. These innovations have not only improved the accuracy and clarity of X-ray images, but also reduced radiation exposure for patients.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Peering into the Soft Tissues
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful medical imaging technology that allows healthcare professionals to peer into the body’s soft tissues. Unlike X-rays, which primarily capture images of bones and dense structures, MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed pictures of organs, muscles, nerves, and other soft tissues.
This non-invasive procedure can provide valuable diagnostic information for various conditions, including tumors, infections, and brain and spinal cord abnormalities. MRI has undergone significant advancements in recent years, with improved image quality and faster scanning times, making it an essential tool in modern medical practice. Its ability to provide detailed anatomical information without ionizing radiation makes it particularly suitable for pediatric patients and individuals sensitive to radiation exposure.
Computed Tomography (CT): Unraveling Three-Dimensional Anatomy
Computed Tomography (CT) technology has revolutionized medical imaging by providing detailed, three-dimensional images of the human body. Using a combination of X-rays and computer processing, CT scans allow healthcare professionals to visualize internal structures with exceptional clarity. This technology is beneficial for diagnosing conditions involving the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis, and extremities.
By unraveling the three-dimensional anatomy of the body, CT scans can detect abnormalities such as tumors, fractures, and infections that may not be visible on traditional X-rays. CT scans can also help guide medical procedures such as biopsies and surgeries. With ongoing advancements in CT technology, medical professionals can expect even higher-resolution images and faster scanning times in the future.
Other Imaging Modalities:
-
Ultrasound Imaging Safe and Versatile Imaging Modality
Ultrasound imaging has emerged as a safe and versatile modality in medical imaging innovations. Unlike other imaging techniques, ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it a preferred choice for imaging pregnant women and children. It uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the body’s internal structures, allowing healthcare professionals to visualize organs, tissues, and blood flow.
The versatility of ultrasound is evident in its ability to be used in various medical specialties, including obstetrics, cardiology, and radiology. In addition, ultrasound can be performed at the bedside, making it an accessible and convenient imaging option. With continuous technological advancements, ultrasound imaging continues to evolve and plays a crucial role in diagnostic medicine.
-
Emerging Imaging Modalities From AI to Molecular Imaging
Emerging imaging modalities, such as AI and molecular imaging, are revolutionizing medical imaging technology. Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnostic imaging. By analyzing vast amounts of data and using machine learning algorithms, AI can assist radiologists in detecting abnormalities and making more accurate diagnoses.
Molecular imaging offers a more profound insight into disease processes at a cellular and molecular level. This advanced imaging modalities utilizes specialized tracers that visualize specific molecules or biological processes in the body, providing valuable information regarding disease progression and treatment response. As these emerging modalities continue to develop, they hold the potential to enhance patient care and advance medical research.
-
Nuclear Medicine Peering into Cellular Activity
Nuclear medicine is a branch of medical imaging technology that allows healthcare professionals to peer into cellular activity within the body. Unlike other imaging techniques such as X-ray, MRI, and CT scans, nuclear medicine uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers to diagnose and treat diseases. These radiotracers are injected into the patient’s bloodstream, swallowed, inhaled, and then detected by unique cameras or scanners that create images of the body’s internal structures and functions.
Healthcare professionals can use nuclear medicine to visualize the functioning of organs and tissues at a cellular level. This provides valuable insights for diagnosing and monitoring various conditions like cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. With new technologies and techniques being developed, nuclear medicine continues to advance and improve diagnostic accuracy and treatment effectiveness.
Final Words
The evolution of medical imaging technology has profoundly impacted the field of medicine, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat various medical conditions with greater accuracy and precision. From X-ray to MRI, CT, ultrasound, and nuclear medicine, each imaging modality offers unique benefits and plays a crucial role in patient care. These advancements have not only improved diagnostic accuracy but also enabled earlier detection of diseases, leading to better patient outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in medical imaging that will enhance our ability to diagnose and treat patients effectively.